
Ani DiFranco (IPA: [ˈɑ.ni]) (born Angela Maria Difranco on September 23, 1970) is a singer, guitarist, and songwriter. She is known as a prolific artist (having released seventeen albums in as many years) and is seen by many as a women's rights and feminist icon.
Biography
On July 21, 2006, DiFranco received the "Woman of Courage Award" at the National Organization for Women (NOW) Conference and Young Feminist Summit in Albany, NY. Past winners have included singer and actress Barbra Streisand and Sen. Barbara Boxer, D-Calif. DiFranco is the first musician to receive the award, given each year to a woman who has set herself apart by her contributions to the feminist movement.
DiFranco has been toasted by the Buffalo News as the "Buffalo's leading lady of rock music." The News further said: "Through the Righteous Babe Foundation, DiFranco has backed various grassroots cultural and political organizations, supporting causes ranging from abortion rights to gay visibility."
Since 2003, DiFranco has been nominated four consecutive times for Best Recording Package at the Grammy Awards, one of which she won, in 2004, for Educated Guess.
Recognition
DiFranco's guitar playing is often characterized by a signature staccato style,
Musical style and the "folk" label
Although much of DiFranco's material is autobiographical, it is often also strongly political. Many of her songs are concerned with contemporary social issues such as racism, sexism, sexual abuse, homophobia, reproductive rights, poverty, and war. The combination of personal and political is partially responsible for DiFranco's early popularity among politically active college students, some of whom set up fan pages on the web to document DiFranco's career as early as 1994. Because DiFranco's rapid rise in popularity in the mid-1990s was fueled mostly by personal contact and word of mouth rather than mainstream press, fans often expressed a feeling of community with each other.
DiFranco has expressed political views outside of her music. During the 2000 U.S. presidential election, she encouraged voting for Ralph Nader in non-battleground states. She supported Dennis Kucinich in the 2004 Democratic primaries.
Lyrics and politics
Ownership of Righteous Babe Records allows DiFranco a great deal of artistic freedom. For example, on her 2004 album Educated Guess, DiFranco played all of the instruments, provided all of the vocals, and recorded the album by herself at her home on an analog 8-track reel to reel. She was also involved in much of the artwork and design for the packaging. The only other person involved in the record's musical production was Greg Calbi, who mastered it. she expressed displeasure that what she considers a way to ensure her own artistic freedom was seen by others solely in terms of its financial success.
Label independence
On September 11, 2007, she released the first retrospective of her career, titled Canon and for the first time, a collection of poetry in a book titled Verses.
DiFranco's album, Reprieve, was released on August 8, 2006. It was previously leaked on iTunes for several hours around July 1, 2006, due to an error saying it was released in 2002.
DiFranco performed with Cyndi Lauper on "Sisters of Avalon", a track from Lauper's 2005 collection The Body Acoustic.
She also collaborated with fellow folk singer Dar Williams on "Comfortably Numb", a Pink Floyd cover song from Williams' 2005 album, My Better Self.
Recent work
 Studio albums
Studio albums1994 - An Acoustic Evening With
1997 - Living in Clip
1998 - Women in (E)motion (limited distribution)
2002 - So Much Shouting, So Much Laughter
2004 - Atlanta - 10.9.03 (Official Bootleg series)
2004 - Sacramento - 10.25.03 (Official Bootleg series)
2004 - Portland - 4.7.04 (Official Bootleg series)
2005 - Boston - 11.16.03 (Official Bootleg series)
2005 - Chicago - 1.17.04 (Official Bootleg series)
2005 - Madison - 1.25.04(Official Bootleg series)
2005 - Rome - 11.15.04 (Official Bootleg series)
2006 - Carnegie Hall - 4.6.02 (Official Bootleg series - available in stores)
2007 - Boston - 11.10.06 (Official Bootleg series) Live albums
1996 - More Joy, Less Shame
1999 - Little Plastic Remixes (limited distribution)
2000 - Swing Set EPs
1989 - Demo tape (unreleased) Demos
2002 - Render: Spanning Time with Ani DiFranco
2004 - Trust Videos
2004 - "Self-evident: poesie e disegni"
2007 - Verses Samples
Righteous Babe Records
Category:Righteous Babe artists
 History
History Video games
Video games
 Definition
Definition


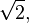
 for the square root of two is better than the quick approximation
for the square root of two is better than the quick approximation  for
for 




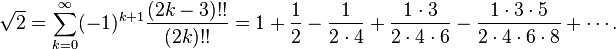


 See also
See also Interior
Interior Career
Career Gallery
Gallery

 44-60
44-60 Emigration system
Emigration system
